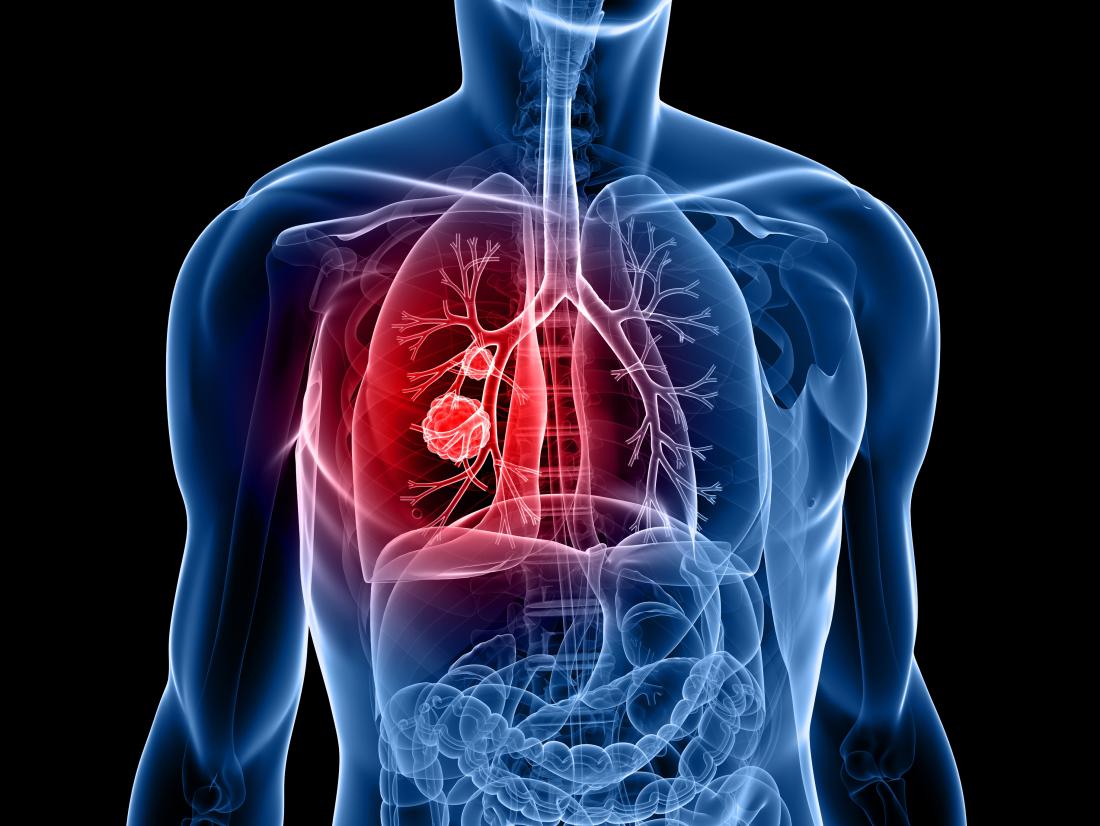
What Is Lung Cancer?
Cellular breakdown in the lungs kills a bigger number of men than some other type of malignant growth. In ladies, it is the subsequent driving reason for disease passing, after bosom malignant growth. Cellular breakdown in the lungs typically begins between the ages of 65 and 75.
Most cellular breakdowns in the lungs start in the bronchi, the aviation routes prompting the lungs. There are different sorts of cellular breakdown in the lungs. The most well-known is squamous cell carcinoma. Different sorts of cellular breakdown in the lungs are little cell carcinoma or anaplastic little cell disease, adenocarcinoma, and huge cell carcinoma.
Each type develops at a different rate and responds differently to treatment. With the exception of adenocarcinoma, most lung cancers are linked to smoking. It is also common for cancer to spread to the lungs from other parts of the body.
Causes and risk factors
Smoking is the cause of over 80% of lung cancer. It is estimated that smokers are 10 to 30 times more exposed to lung cancer than the general population. Cigar and pipe are almost as conducive to lung cancer as cigarettes. Even exposure to second-hand smoke – the smoke exhaled by smokers and produced by their cigarettes – can cause lung cancer.
Living in an environment where air pollution is high or working with radioactive minerals or asbestos can also increase the risk of cancer. These risk factors cause certain DNA changes in lung cells, causing them to grow abnormally and form cancer.
Symptoms and complications
The first and most common symptom of lung cancer is the onset of a cough.
The other symptoms are as follows:-
- presence of blood in the sputum (sputum);
- wheezing;
- chest pain;
- pneumonia (symptoms: cough, fever, chest pain and shortness of breath); and
- loss of appetite, weakness and weight loss.
Cellular breakdown in the lungs can spread to parts of the body close to the lungs or to different pieces of the body, like the liver, mind and bones, causing torment and different difficulties, like cardiovascular breakdown. breathing troubles and nerve harm. A few tumors additionally discharge chemicals that can influence the body’s digestion.
Diagnostic
Lung cancer is usually suspected when a chest x-ray shows a shadow on the lung.
To confirm the diagnosis, a doctor examines the patient’s sputum. A lesion (area where tissue is damaged or abnormal) that is visible on X-ray can be confirmed with a CT scan of the lungs; one can also introduce, under scintigraphic control, a long needle in the lung in order to carry out a biopsy (taking of a sample) of the lesion.
The doctor usually examines the lungs with an instrument inserted into the bronchi; such an examination is called a bronchoscopy. A biopsy can also be done during the bronchoscopy. A biopsy involves taking a sample of tissue from the tumor which will then be examined under a microscope. These tissues can also be collected through surgery on the chest. If you have any questions about diagnosing lung cancer, consult your doctor.
Processing
Lung cancer can be treated with surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy, either alone or in combination, depending on the stage of the tumor. The most suitable treatment (s) will depend on the type of lung cancer, the stage of the disease (more or less advanced cancer), your general health, side effects and the potential for a cure, symptom relief or life extension. Ask your doctor to tell you about possible treatments.
Surgery
Surgery can only be done if the tumor is small and confined to one lung, and the other lung is strong enough to function on its own. This type of procedure is called a pneumonectomy if the entire lung is excised (removed) and a lobectomy if only part of the lung is removed. The doctor determines how much lung tissue needs to be excised during the procedure.
While 10% to 35% of lung cancers can be excised surgically, surgery cannot always cure the disease. It is recommended only in patients who are reasonably healthy and do not have any signs of the tumor spreading. If the person has a serious heart problem or suffers from other lung disease, surgery may need to be ruled out.



Average Rating